Publications
Multiscale analyses reveal native-like lamellar bone repair and near perfect bone-contact with porous strontium-loaded bioactive glass
H Autefage, F Allen, HM Tang, C Kallepitis, E Gentleman, N Reznikov, K Nitiputri, A Nommeots-Nomm, MD O’Donnell, Claudia Lange, BM Seidt, TB Kim, AK Solanki, F Tallia, G Young, PD Lee, BF Pierce, Wolfgang Wagermaier, Peter Fratzl, A Goodship, JR Jones, G Blunn, MM Stevens
Biomaterials 209, 152-162 (2019)
Abstract
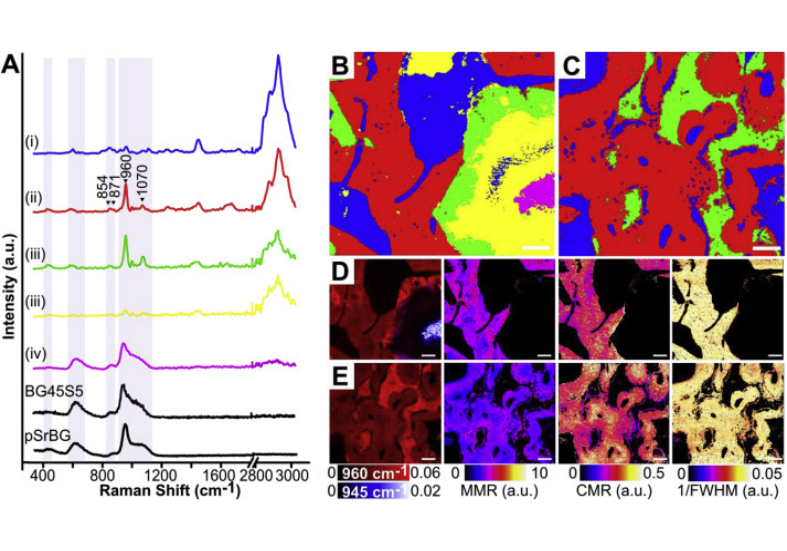
The efficient healing of critical-sized bone defects using synthetic biomaterial-based strategies is promising but remains challenging as it requires the development of biomaterials that combine a 3D porous architecture and a robust biological activity. Bioactive glasses (BGs) are attractive candidates as they stimulate a biological response that favors osteogenesis and vascularization, but amorphous 3D porous BGs are difficult to produce because conventional compositions crystallize during processing. Here, we rationally designed a porous, strontium-releasing, bioactive glass-based scaffold (pSrBG) whose composition was tailored to deliver strontium and whose properties were …
Cell-geometry-dependent changes in plasma membrane order direct stem cell signalling and fate
Thomas C von Erlach, Sergio Bertazzo, Michele A Wozniak, Christine-Maria Horejs, Stephanie A Maynard, Simon Attwood, Benjamin K Robinson, Hélène Autefage, Charalambos Kallepitis, Armando del Río Hernández, Christopher S Chen, Silvia Goldoni, Molly M Stevens
Nature materials 17 (3), 237-242 (2018)
Abstract
Cell size and shape affect cellular processes such as cell survival, growth and differentiation, thus establishing cell geometry as a fundamental regulator of cell physiology. The contributions of the cytoskeleton, specifically actomyosin tension, to these effects have been described, but the exact biophysical mechanisms that translate changes in cell geometry to changes in cell behaviour remain mostly unresolved. Using a variety of innovative materials techniques, we demonstrate that the nanostructure and lipid assembly within the cell plasma membrane are regulated by cell geometry in a ligand-independent manner. These biophysical changes trigger signalling events involving the …
Cobalt-containing bioactive glasses reduce human mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation despite HIF-1α stabilisation
E Littmann, H Autefage, AK Solanki, C Kallepitis, Julian R Jones, M Alini, M Peroglio, Molly M Stevens
Journal of the European Ceramic Society 38 (3), 877-886 (2018)
Abstract
Bioactive glasses (BGs) are excellent delivery systems for the sustained release of therapeutic ions and have been extensively studied in the context of bone tissue engineering. More recently, due to their osteogenic properties and expanding application to soft tissue repair, BGs have been proposed as promising materials for use at the osteochondral interface. Since hypoxia plays a critical role during cartilage formation, we sought to investigate the influence of BGs releasing the hypoxia-mimicking agent cobalt (CoBGs) on human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSC) chondrogenesis, as a novel approach that may guide future osteochondral scaffold design. The CoBG dissolution products significantly increased the level of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in hMSCs in a cobalt dose-dependent manner. Continued exposure to the cobalt-containing BG extracts …
Distinct bimodal roles of aromatic molecules in controlling gold nanorod growth for biosensing
Jun Hui Soh, Yiyang Lin, Michael R Thomas, Nevena Todorova, Charalambos Kallepitis, Irene Yarovsky, Jackie Y Ying, Molly M Stevens
Advanced Functional Materials 27 (29), 1700523 (2017)
Abstract
New aromatic molecule–seed particle interactions are examined and exploited to control and guide seed‐mediated gold nanorod (Au NR) growth. This new approach enables better understanding of how small molecules impact the synthesis of metallic nanostructures, catalyzing their use in various biomedical applications, such as plasmonic biosensing. Experimental studies and theoretical molecular simulations using a library of aromatic molecules, making use of the chemical versatility of the molecules with varied spatial arrangements of electron‐donating/withdrawing groups, charge, and Au‐binding propensity, are performed. Au NR growth is regulated by two principal mechanisms, producing either a red or blue shift in the longitudinal localized surface plasmon resonance (LLSPR) peaks. Aromatic molecules with high redox potentials produce an increase in NR aspect ratio …
Quantitative volumetric Raman imaging of three dimensional cell cultures
Charalambos Kallepitis, Mads S Bergholt, Manuel M Mazo, Vincent Leonardo, Stacey C Skaalure, Stephanie A Maynard, Molly M Stevens
Nature communications 8 (1), 1-9 (2017)
Abstract
The ability to simultaneously image multiple biomolecules in biologically relevant three-dimensional (3D) cell culture environments would contribute greatly to the understanding of complex cellular mechanisms and cell–material interactions. Here, we present a computational framework for label-free quantitative volumetric Raman imaging (qVRI). We apply qVRI to a selection of biological systems: human pluripotent stem cells with their cardiac derivatives, monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages in conventional cell culture systems and mesenchymal stem cells inside biomimetic hydrogels that supplied a 3D cell culture environment. We demonstrate visualization and quantification of fine details in cell shape, cytoplasm, nucleus, lipid bodies and cytoskeletal structures in 3D with unprecedented biomolecular specificity for vibrational microspectroscopy.
Fibres and cellular structures preserved in 75-million–year-old dinosaur specimens
Sergio Bertazzo, Susannah CR Maidment, Charalambos Kallepitis, Sarah Fearn, Molly M Stevens, Hai-nan Xie
Nature Communications 6, 7352 (2015)
Abstract
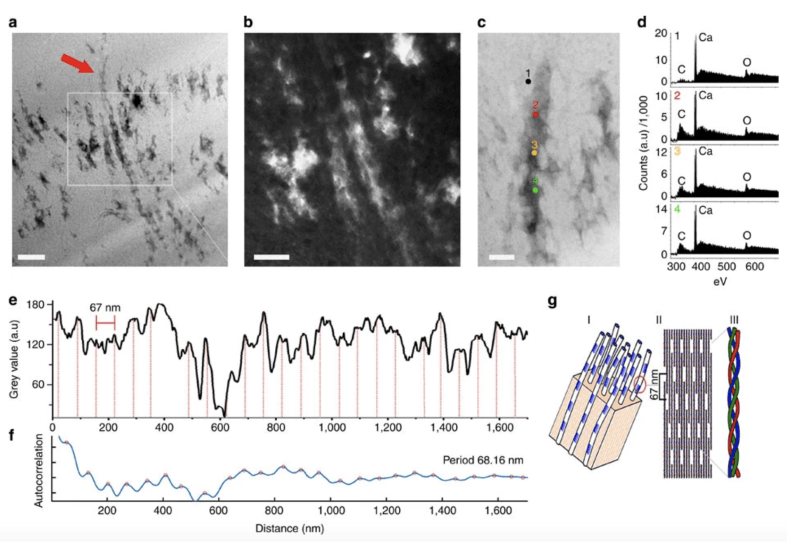
Exceptionally preserved organic remains are known throughout the vertebrate fossil record, and recently, evidence has emerged that such soft tissue might contain original components. We examined samples from eight Cretaceous dinosaur bones using nano-analytical techniques; the bones are not exceptionally preserved and show no external indication of soft tissue. In one sample, we observe structures consistent with endogenous collagen fibre remains displaying∼ 67 nm banding, indicating the possible preservation of the original quaternary structure. Using ToF-SIMS, we identify amino-acid fragments typical of collagen fibrils. Furthermore, we observe structures consistent with putative erythrocyte remains that exhibit mass spectra similar to emu whole blood. Using advanced material characterization approaches, we find that these putative biological structures can be well …
Differentiating sepsis from non-infectious systemic inflammation based on microvesicle-bacteria aggregation
Inge K Herrmann, Sergio Bertazzo, David JP O’Callaghan, Andrea A Schlegel, Charalambos Kallepitis, David B Antcliffe, Anthony C Gordon, Molly M Stevens
Nanoscale 7 (32), 13511-13520 (2015)
Abstract
Sepsis is a severe medical condition and a leading cause of hospital mortality. Prompt diagnosis and early treatment has a significant, positive impact on patient outcome. However, sepsis is not always easy to diagnose, especially in critically ill patients. Here, we present a conceptionally new approach for the rapid diagnostic differentiation of sepsis from non-septic intensive care unit patients. Using advanced microscopy and spectroscopy techniques, we measure infection-specific changes in the activity of nano-sized cell-derived microvesicles to bind bacteria. We report on the use of a point-of-care-compatible microfluidic chip to measure microvesicle-bacteria aggregation and demonstrate rapid (≤1.5 hour) and reliable diagnostic differentiation of bacterial infection from non-infectious inflammation in a double-blind pilot study. Our study demonstrates the potential of …